Finite Element
The first and most crucial step in finite element micromagnetics is mesh generation. Several software tools are available for mesh generation. Here we introduce two primary options:
1. Netgen
Repository: https://github.com/NGSolve/netgen
Documentation: https://github.com/NGSolve/netgen/blob/master/doc/ng4.pdf
Typical Usage (creates hemisphere):
ng
algebraic3d
solid hemisphere = sphere (1, 0, 0; 10) and plane (1, 0, 0; 0, 0, -1);
tlo hemisphere -maxh=2.0;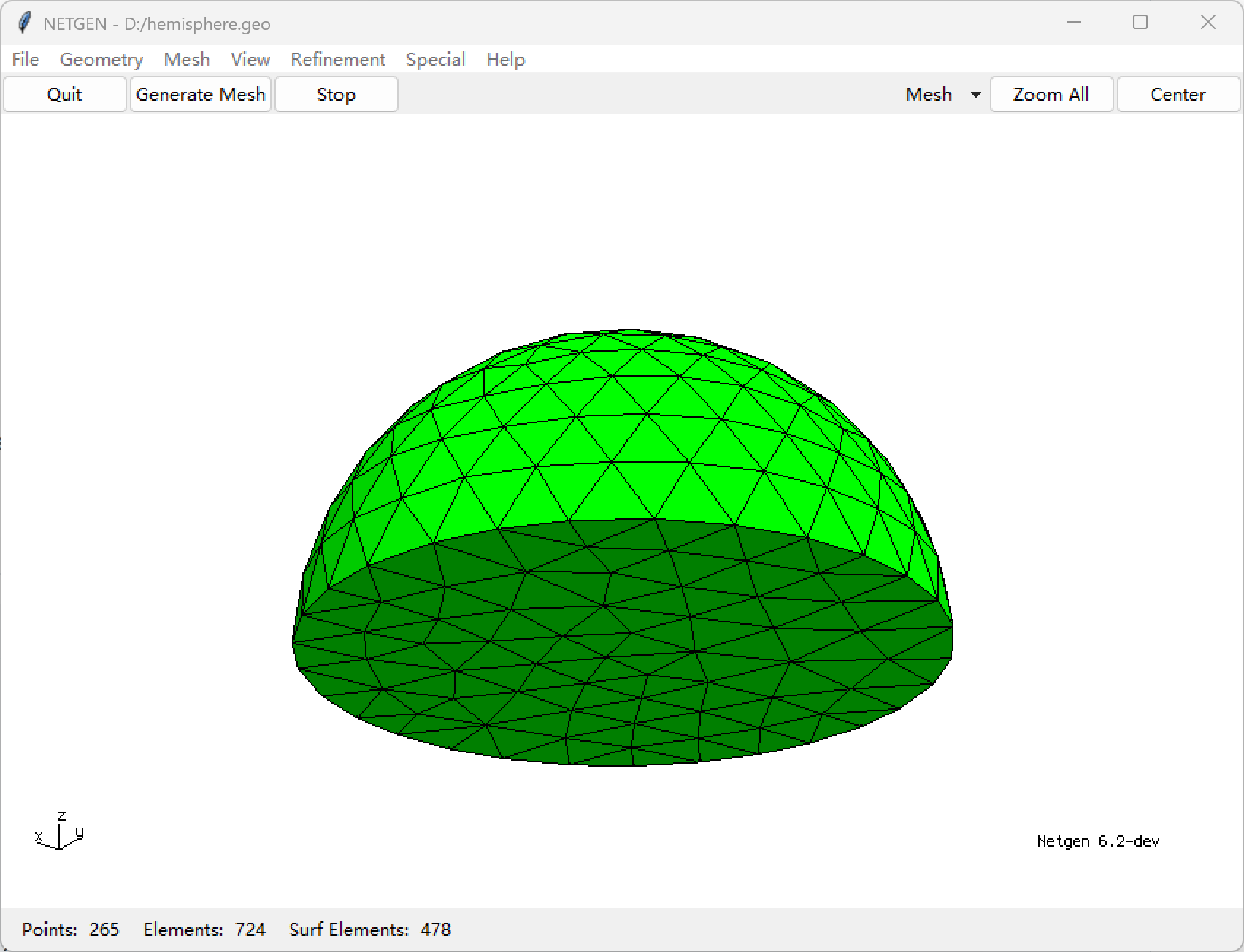
MicroMagnetic.jl natively supports Netgen's Neutral format.
2. Gmsh
Website: https://gmsh.info/
Tutorial: https://gmsh.info/dev/doc/texinfo/gmsh.html#Gmsh-tutorial
Gmsh supports OpenCASCADE geometry kernel, enabling direct creation of complex shapes. Below is a modified Julia example generating the same hemisphere and exporting to Gmsh format:
julia
using Gmsh
gmsh.initialize()
gmsh.model.add("hemisphere")
# Create sphere and cutting box
sphere_tag = gmsh.model.occ.addSphere(1, 0, 0, 10)
box_tag = gmsh.model.occ.addBox(-100, -100, 0, 200, 200, 100) # Large cutting box
# Perform boolean cut operation
hemisphere, _ = gmsh.model.occ.cut(
[(3, sphere_tag)], # Original sphere (dim=3)
[(3, box_tag)] # Cutting tool (dim=3)
)
gmsh.model.occ.synchronize()
# Generate mesh with size constraints
gmsh.option.setNumber("Mesh.MeshSizeMax", 2.0)
gmsh.model.mesh.generate(3)
# Export in Gmsh format
gmsh.write("hemisphere.msh")
gmsh.write("hemisphere.vtk")
gmsh.finalize()The vtk file can be opened using Paraview, as follows: